6-5-2. MINIMA ON DIVERGING RADIALS
- Views Views: 975
- Last updated Last updated:
-
6-5-2. MINIMA ON DIVERGING RADIALS
- Consider separation to exist between aircraft:
- Established on radials of the same NAVAID that diverge by at least 15 degrees when either aircraft is clear of the airspace to be protected for the other aircraft.
- With non-VOR/DME based navigational equipment established on tracks of the same waypoint that diverge by at least 15 degrees when either aircraft is clear of the airspace to be protected for the other aircraft.
FIG 6-5-1 Minima on Diverging Radials 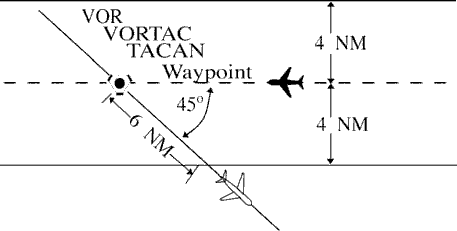
NOTE: The procedure may be applied to converging as well as diverging aircraft. (See FIG 6-5-1.) The aircraft depicted 6 miles from the NAVAID/waypoint would require vertical separation until reaching the 6-mile point. Reversing direction, the same aircraft would require vertical separation before passing the 6-mile point. Due to the nature of GPS equipment, issue crossing restrictions in reference to the next waypoint, since the pilot receives tracking “to” data rather than tracking “from” the last waypoint.
- Use TBL 6-5-1 and TBL 6-5-2 to determine the distance required for various divergence angles to clear the airspace to be protected. For divergence that falls between two values, use the lesser divergence value to obtain the distance.
TBL 6-5-1 Non-DME Divergence Distance Minima Divergence (Degrees) Distance (NM) 15 16 20 12 25 10 30 8 35 7 45 6 55 5 90 4 NOTE: This table is for non-DME application only. TBL 6-5-2 Divergence Distance Minima Divergence (Degrees) Distance (NM) Below FL 180 Fl 180 through FL 450 15 17 18 20 13 15 25 11 13 30 9 11 35 8 11 45 7 11 55 6 11 90 5 11 NOTE: This table is for DME application and compensates for DME slant-range error. NOTE: For altitudes of 3,000 feet or less above the elevation of the NAVAID, DME slant-range error is negligible and the values in TBL 6-5-1 may be used.
- Consider separation to exist between aircraft: