8-3-2. SEPARATION METHODS
- Views Views: 903
- Last updated Last updated:
-
8-3-2. SEPARATION METHODS
-
For the purpose of application of longitudinal separation, the terms same track must be considered identical to
same course, reciprocal tracks must be considered identical to reciprocal courses, and crossing tracks, must be
considered identical to crossing courses.
NOTE: Refer to paragraph 1-2-2, Course Definitions.
-
Separate aircraft longitudinally in accordance with the following:
-
Same track. Ensure that the estimated spacing between aircraft is not less than the applicable minimum
required. (See FIG 8-3-1.)
FIG 8-3-1 Same Courses 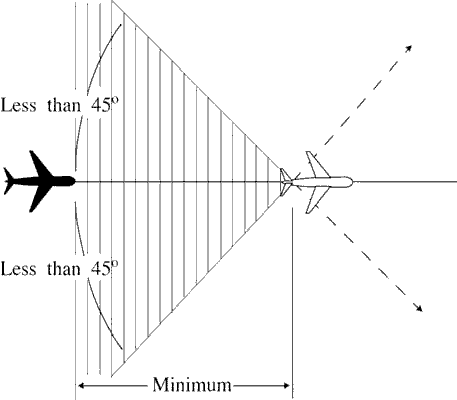
-
Crossing tracks. Ensure that the estimated spacing at the point of intersection is not less than the
applicable minimum required. (See FIG 8-3-2.)
FIG 8-3-2 Crossing Courses 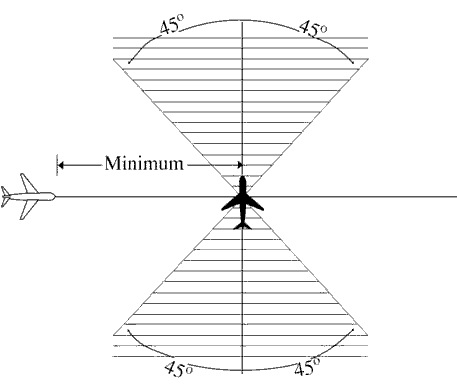
-
Reciprocal tracks:
-
(a) Ensure that aircraft are vertically separated for a time interval equal to the applicable minimum
required before and after the aircraft are estimated to pass. (See FIG 8-3-3.)
FIG 8-3-3 Reciprocal Courses 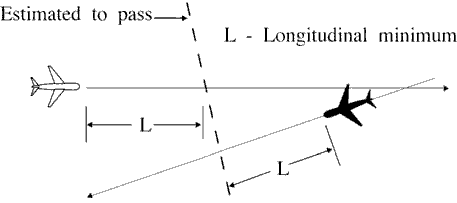
-
(b) Vertical separation may be discontinued after one of the following conditions is met:
-
(1) Both aircraft have reported passing a significant point and the aircraft are separated by at least
the applicable minimum required for the same direction longitudinal spacing; (See FIG 8-3-4.) or
FIG 8-3-4 Vertical Separation 
- (2) Both aircraft have reported passing ground-based NAVAIDs or DME fixes indicating that they have passed each other.
-
(1) Both aircraft have reported passing a significant point and the aircraft are separated by at least
the applicable minimum required for the same direction longitudinal spacing; (See FIG 8-3-4.) or
-
(a) Ensure that aircraft are vertically separated for a time interval equal to the applicable minimum
required before and after the aircraft are estimated to pass. (See FIG 8-3-3.)
-
Same track. Ensure that the estimated spacing between aircraft is not less than the applicable minimum
required. (See FIG 8-3-1.)
-
For the purpose of application of longitudinal separation, the terms same track must be considered identical to
same course, reciprocal tracks must be considered identical to reciprocal courses, and crossing tracks, must be
considered identical to crossing courses.